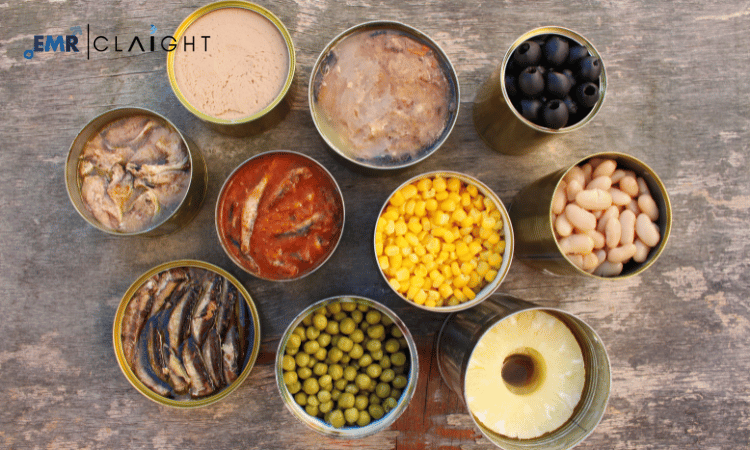

The canned food industry has witnessed substantial growth over the years, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient, long-lasting, and easy-to-prepare food products. Canned foods, which range from vegetables and fruits to meats, soups, and beverages, offer numerous benefits, including extended shelf life and the ability to store seasonal products year-round. A Canned Food Manufacturing Plant Project represents a significant investment opportunity, tapping into the growing global trend of ready-to-eat and packaged foods. This article delves into the essential components and considerations involved in setting up a successful canned food manufacturing plant, focusing on everything from production processes to market opportunities.
Understanding the Canned Food Industry
The canned food industry has evolved from being a niche market to a global staple in households, restaurants, and retail stores. The primary appeal of canned food lies in its convenience. It requires minimal preparation, can be stored for long periods without refrigeration, and is available in a wide range of varieties. Canned foods help reduce food wastage by preserving nutrients, flavor, and texture of products. These products are often subjected to pasteurization or sterilization processes, ensuring that they remain safe to consume for extended periods.
With busy lifestyles becoming more common, many consumers prefer the convenience offered by canned foods. The growing demand for ready-to-eat meals, especially in urban populations, has led to increased consumption of canned goods. Additionally, the rising trend of health-conscious eating has encouraged the production of canned food options that are organic, preservative-free, or feature healthier alternatives.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/canned-food-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Market Trends and Growth Potential
The global canned food market is poised for growth, driven by several factors. A significant driver is the increasing demand for processed and packaged foods, particularly among the working population, who seek convenience without compromising on food quality. Canned food manufacturers have responded to these demands by introducing innovative products, such as organic, low-sodium, and preservative-free canned foods, catering to health-conscious consumers.
Emerging markets in Asia Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are also experiencing a surge in demand for canned foods, largely due to rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable income. For instance, in countries like India and China, where traditional cooking methods remain prevalent, canned food offers a quicker and more convenient option for consumers.
The market is also evolving to meet specific dietary needs, such as gluten-free, vegan, and low-calorie options. Manufacturers are continually working on product diversification to cater to a broader demographic. Additionally, the rise in e-commerce and online grocery shopping has also provided new avenues for canned food distribution, reaching an even larger consumer base.
Key Components of a Canned Food Manufacturing Plant
Setting up a Canned Food Manufacturing Plant involves several key steps, ranging from sourcing raw materials to ensuring regulatory compliance. Each stage of production is crucial to ensuring that the final product meets industry standards for safety, quality, and taste.
1. Raw Material Sourcing and Procurement
The foundation of any canned food product lies in its raw materials. The types of raw materials depend on the specific product being manufactured. For instance, vegetables, fruits, meats, fish, and beans are common ingredients in canned food production. Sourcing high-quality raw materials is vital for maintaining the taste, texture, and nutritional value of the canned product.
Suppliers should be selected based on their ability to provide consistent and quality raw materials. In some cases, local sourcing might be preferred to reduce costs and improve supply chain efficiency. Additionally, sustainable sourcing practices can be incorporated to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and meet certification standards for organic and eco-friendly products.
2. Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for canned food typically involves the following stages:
-
Preparation and Sorting: Raw materials are cleaned, sorted, and prepped for the canning process. This may involve washing, peeling, cutting, or blanching the food items to prepare them for preservation. For fruits and vegetables, blanching helps preserve the color, texture, and nutritional value of the product.
-
Filling: Once the food is prepared, it is placed into sterilized cans, either manually or using automated machinery. The cans are filled to the desired level, ensuring that the correct portion of food is contained within each package. For meats and fish, this step may also involve adding a liquid, such as brine, syrup, or oil, to preserve the food and enhance its flavor.
-
Sealing and Sterilization: The cans are sealed tightly to prevent contamination and preserve freshness. Sterilization, often achieved through high-heat processes like pasteurization or autoclaving, ensures that the food remains safe for consumption for extended periods. This process eliminates harmful bacteria and other microorganisms that could compromise the safety of the product.
-
Cooling: After sterilization, the cans are rapidly cooled to prevent the growth of any remaining microorganisms. This is typically done by immersing the cans in cold water or using air cooling systems.
-
Labeling and Packaging: Once the cans have been sterilized and cooled, they are labeled with product information, including ingredients, expiration dates, and any relevant certifications (such as organic or gluten-free). The final packaged products are then ready for distribution.
Throughout the production process, quality control is essential to ensure that the final product is safe, nutritious, and of the highest quality. Routine checks are performed at various stages of production, including raw material inspection, monitoring cooking times and temperatures, and final product testing.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control
Compliance with food safety standards and regulations is critical for any food manufacturing plant. Canned food products must meet specific guidelines set by local and international regulatory agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), and local health departments.
Key regulations include adherence to safe food handling practices, proper sanitation procedures, and ensuring that labeling is accurate and transparent. Additionally, food manufacturers must comply with specific certifications related to product safety, such as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), which helps identify and control potential food safety hazards throughout the production process.
Regular audits and inspections by regulatory bodies ensure that manufacturers maintain high standards and consistently meet the requirements for food safety and quality.
4. Packaging and Distribution
Packaging plays a crucial role in preserving the quality and safety of canned food. The packaging must be durable enough to withstand transportation and handling while providing an airtight seal to prevent spoilage. Materials used in packaging must meet food safety standards and be non-toxic.
The distribution network for canned food involves transportation to wholesalers, retailers, and supermarkets. Efficient logistics systems ensure that products reach the market on time while maintaining their quality. With the rise of online shopping, many canned food manufacturers have also started offering direct-to-consumer services through e-commerce platforms, reaching a broader audience.
5. Sustainability Considerations
As consumer preferences shift towards more environmentally friendly options, sustainability has become a significant factor in the canned food industry. Manufacturers are increasingly looking at ways to reduce their environmental impact through energy-efficient manufacturing processes, waste reduction, and sustainable sourcing of raw materials.
For example, recyclable packaging, reduced water usage, and the use of renewable energy sources in production can significantly lower the carbon footprint of a canned food manufacturing plant. Additionally, companies are responding to consumer demand for organic and non-GMO products by incorporating these options into their product lines.
Market Entry and Competitive Strategies
Entering the canned food market requires a strategic approach, as the competition is intense. Companies must differentiate themselves through product quality, innovative packaging, and effective marketing strategies. Focusing on consumer preferences, such as organic or healthier canned food options, can provide a competitive edge.
Marketing efforts should target both traditional retail channels and the growing online marketplace. Collaborating with retailers and developing strong relationships with distributors are crucial for market penetration. Offering product samples, running promotional campaigns, and emphasizing health benefits can also help boost brand recognition and consumer loyalty.
A Canned Food Manufacturing Plant Project offers a promising opportunity for businesses looking to tap into the growing demand for packaged and ready-to-eat foods. With the right strategy, focusing on product quality, compliance with food safety standards, and sustainable practices, manufacturers can succeed in this competitive industry. By catering to evolving consumer preferences and staying ahead of market trends, companies can carve out a strong position in the global canned food market.




Leave a Reply